Cardiology, the medical specialty devoted to diagnosing a 通波仔 nd treating heart disorders, is akin to an intricate symphony, where each section plays a vital role in maintaining the harmony of the cardiovascular system. This field encompasses a broad range of conditions, from congenital anomalies to acquired diseases, and requires a deep understanding of the heart’s anatomy and physiology. Advances in cardiology have revolutionized how we approach heart health, leading to improved outcomes and innovative treatments that continue to evolve.
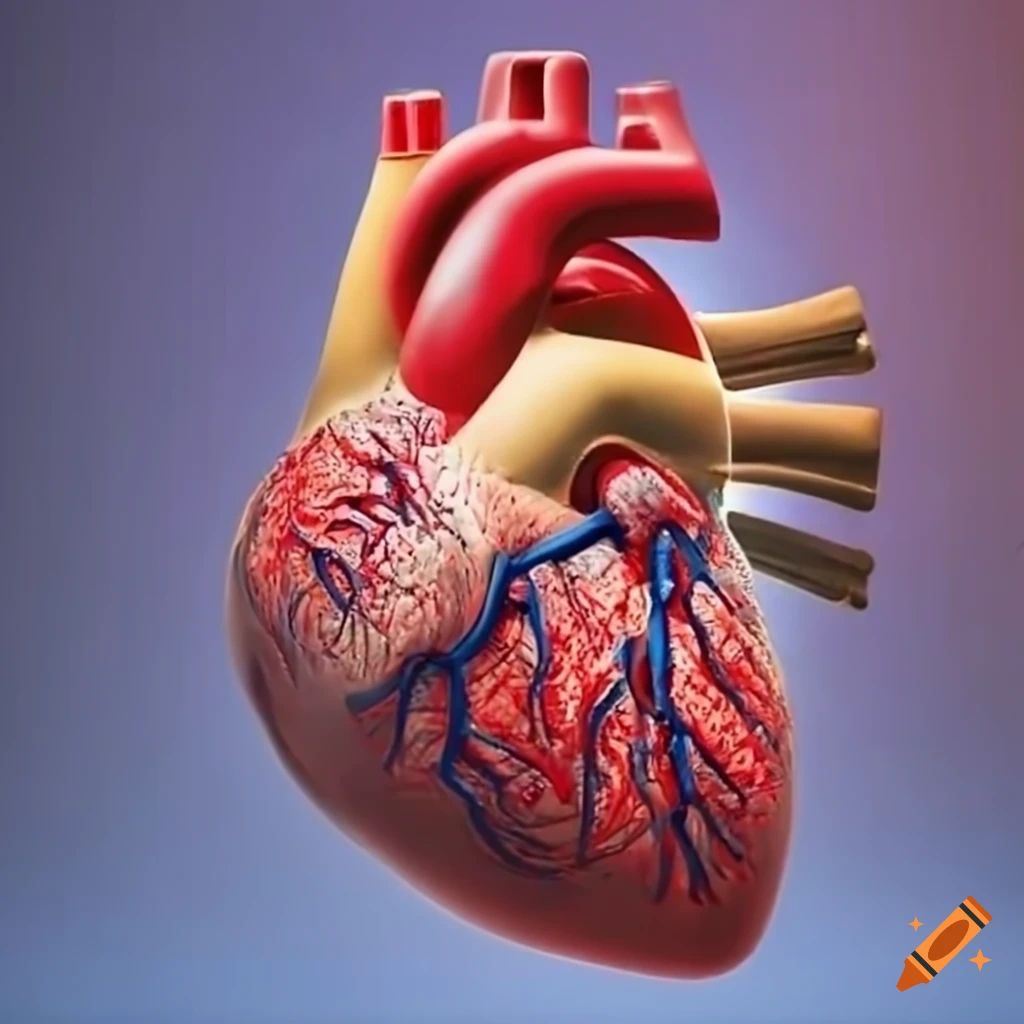
One of the primary focuses in cardiology is the management of coronary artery disease (CAD), a condition characterized by the narrowing of the coronary arteries due to plaque buildup. This blockage can lead to angina, heart attacks, and other serious complications. Cardiologists employ a variety of diagnostic tools, including stress tests, echocardiograms, and coronary angiograms, to assess the severity of CAD and determine the most effective treatment strategy. Lifestyle modifications, pharmacological interventions, and surgical procedures like angioplasty and stenting are commonly used to alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is another critical area of concern in cardiology. Often dubbed the “silent killer, ” hypertension can lead to severe complications such as heart failure, stroke, and kidney damage if left untreated. Cardiologists emphasize the importance of regular monitoring and early intervention to manage blood pressure levels effectively. Treatment usually involves a combination of lifestyle changes, such as dietary adjustments and increased physical activity, alongside medications designed to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of associated health problems.
Heart failure, a condition where the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, represents a major challenge in cardiology. It can result from various underlying issues, including coronary artery disease, hypertension, and valvular heart disease. Managing heart failure requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication management, lifestyle modifications, and sometimes advanced therapies such as implantable devices or heart transplants. The goal is to improve the patient’s quality of life, alleviate symptoms, and slow the progression of the disease.
The future of cardiology is promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements paving the way for new treatments and diagnostic tools. Innovations such as wearable heart monitors, advanced imaging techniques, and minimally invasive surgical options are transforming how cardiologists approach heart disease. As our understanding of cardiovascular health continues to expand, the field of cardiology will undoubtedly evolve, offering hope for even better outcomes and a higher quality of life for patients worldwide.
